Can an at-home vagus nerve stimulator scale back stress? Inside the brand new tech

Thank u, necks!
Urgent a $269 electrical system in opposition to the vagus nerve in your neck will be the secret to good vibes and stellar sleep.
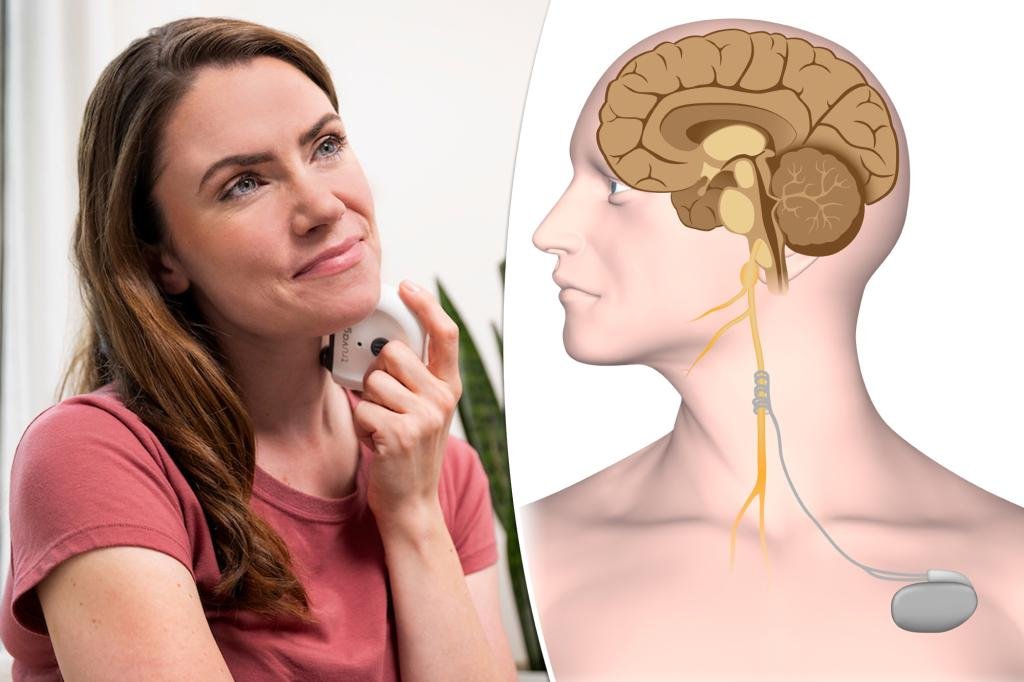
Implantable vagus nerve stimulation (VNS) units, which may value $50,000, have lengthy been used to deal with epilepsy, melancholy and stroke. That’s as a result of jolting the vagus nerve — the longest cranial nerve within the physique — can assist regulate mind exercise, scale back irritation and calm the nervous system.
Now, a brand new crop of buzzy non-invasive VNS devices guarantees to alleviate stress, sharpen focus and enhance sleep in mere minutes for a fraction of the price. Nonetheless, scientists warn that extra analysis is required to totally perceive the effectiveness and potential purposes of those business instruments.
“The science remains to be very younger,” Timir Datta, assistant professor within the Institute of Bioelectronic Drugs on the Feinstein Institutes for Medical Analysis, informed The Put up.
Right here’s every part it’s essential to find out about this fashionable remedy, a part of the $8.3 billion neurostimulation market.
What’s vagus nerve stimulation?
Datta describes the vagus nerve as a bundle of fibers stretching from the mind to the intestine.
The vagus is a vital part of the parasympathetic nervous system, primarily accountable for the physique’s leisure response and involuntary actions like respiratory, coronary heart price and digestion.
Sending electrical impulses to the vagus can affect ranges of neurotransmitters within the mind like norepinephrine and serotonin, probably bettering temper. VNS has been known as a “pacemaker for the mind.”
“Vagus nerve stimulation pulls you out of that demanding physiologic state. It places you right into a extra metabolically secure and wholesome state,” Dr. Peter Staats — chief medical officer for Truvaga, a handheld VNS system that launched in 2022 — informed The Put up.
How do the units work?
VNS units implanted surgically are programmed to fireplace delicate, temporary electrical pulses to the brainstem at common intervals, like each 5 minutes.
Truvaga is beneficial to be used twice day by day, with every session lasting two minutes. Pulsetto, a wearable gadget, wants “solely 4 minutes to scale back stress.” Two or three day by day periods are suggested for optimum outcomes.
There are different key variations between implantable and handheld VNS.
“Because the implantable ones are proper up in opposition to the nerve, you possibly can just about be assured that they’re going to be doing one thing to the vagus nerve,” Datta defined.
With the non-invasive units, “there’s a number of different tissue in between,” he continued. “There’s, clearly, your pores and skin, every other tissue, muscle, fats that you simply may need between the stimulator itself and the nerve, so the way in which that it engages the nerve just isn’t as effectively understood.”
Value and potential downsides additionally range.
“An implanted system prices about $50,000 and has a big threat. There’s a threat of harm to what’s known as the recurrent laryngeal nerve, which lets you communicate and might trigger hoarseness if it’s broken,” Staats mentioned. “With non-invasive [gadgets], the dangers are exceedingly low, they usually’re comparatively cheap.”
Truvaga 350, which permits for 350 two-minute stimulation periods, retails for $299. Truvaga Plus, which boasts limitless periods and different options, prices $499.
Pulsetto is priced at $269. A premium subscription package deal, which incorporates personalised applications, is bought individually.
Unwanted side effects of non-invasive units embody pores and skin irritation, delicate complications, throat discomfort, a tingling sensation, dizziness and nausea.
How efficient are they?
The US Meals and Drug Administration authorised the primary VNS system, an implanted pulse generator, in 1997 to deal with seizures. Since then, the FDA has cleared non-invasive units to deal with cluster complications and respiratory troubles from COVID-19.
Analysis on potential makes use of for the transportable units continues.
“For those who had been to check out issues like sleep, nervousness, dependancy, migraine complications, cluster complications, post-traumatic stress dysfunction, a lot of the research on these therapies are with non-invasive approaches,” Staats mentioned.
He mentioned “it’s most likely a lot safer” to do VNS than to take medication to deal with these situations.
Datta suggests ready “for the science to be a bit of bit extra developed” earlier than buying a VNS system until your physician particularly recommends one.
For non-invasive VNS to work, you have to find the vagus nerve. For those who can’t discover it, you possibly can’t stimulate it after which you could have a pricey paperweight. VNS sellers supply assist to these having hassle.
First, really feel both aspect of your neck for a bump, bump, bump, which is the carotid artery. The vagus runs parallel to the carotid artery. Subsequent, spray or put gel on the pores and skin of your neck earlier than making use of the system.
Alternative routes to stimulate the vagus
These stimulators aren’t for everybody. Staats mentioned Truvaga might not be appropriate for individuals with defibrillator pacemakers.
“We’ve not seen any interplay with the pacemaker but, however that’s the one which retains me up at night time,” Staats mentioned. He’s involved “that someway there’s going to be an electrical subject that’s created that the sensor in your coronary heart with the pacemaker perceives as an arrhythmia after which shocks the affected person. We’ve not seen that occur, however that’s what I fear about.”
For these not prepared or suggested to make the leap with VNS, the vagus nerve might be activated by loud singing, buzzing, chanting, gargling water, taking sluggish, deep breaths from the stomach, practising yoga, immersing in chilly water and getting a therapeutic massage.