California mushroom poisonings are on the rise. Here is what’s being executed to curb publicity

David Yturralde arrived on the mushroom discuss in Newport Seaside just lately armed with a pen and paper and a bunch of questions. The objective, he mentioned, was to demystify these fascinating fungi that popped up on his grass after heavy winter rain.
He’s lengthy been within the mushrooms that sprout on the entrance garden of his San Clemente residence, however he’s all the time been too timid to select any. And there’s no approach he’s gathering any to style, he mentioned.
“Mushrooms are mysterious little issues as a result of immediately your mother and father let you know, as a baby, don’t eat that,” he mentioned.
However after listening to about current diseases and fatalities associated to the demise cap mushroom, Amanita phalloides, in California, Yturralde and several other others who gathered within the Environmental Nature Heart’s convention room sought solutions about which mushrooms within the space are lethal.
Previously three months, California has seen a sudden uptick within the variety of folks changing into sickened and dying after by accident consuming toxic mushrooms discovered within the wild. Whereas the fatalities have occurred alongside the Central Coast and in Northern California, the phenomenon has prompted considerations and discussions amongst mycological societies and newbie foragers throughout the Golden State.
The newest demise was reported on Jan. 27 by public well being officers in Contra Costa County who confirmed a 60-year-old man died after consuming wild mushrooms, bringing the overall variety of fungi-related fatalities to 4.
Public well being officers couldn’t determine which wild mushroom precipitated the person’s demise, mentioned Nicola Gillette, spokesperson for Contra Costa Well being. However officers mentioned the person, who was described as being of “Hispanic descent,” died after consuming wild mushrooms foraged at a regional park within the county.
“Preliminary data signifies the person might have mistaken the mushroom for a spread that’s edible in his residence nation,” Gillette mentioned.
The California Division of Public Well being reported 39 demise cap-related diseases, together with 4 fatalities and three liver transplants, between Nov. 18 and Jan. 18.
In a typical yr, the California Poison Management Heart might obtain as much as 5 instances of toxic mushroom-related sickness, in accordance with authorities.
The final main outbreak occurred in 2016 with 14 reported instances, and whereas there have been no deaths, three folks required liver transplants and one little one suffered a “everlasting neurologic impairment.”
On this slew of instances, the California Division of Public Well being has reported that 60% of affected people spoke Spanish as their major language — different affected folks converse Mixteco, Mandarin Chinese language, Ukrainian, Russian and English.
The incidents which have occurred inside the Latino neighborhood this yr could possibly be an anomaly, mentioned Mike McCurdy, president of the San Francisco Mycological Society.
The society has been working intently with the state public well being division to create a warning signal and fliers with a QR code resulting in extra data in a number of languages that may be distributed in leisure areas similar to parks, nature preserves and climbing trails.
Typically, individuals are by accident poisoned after they mistakenly eat a wild mushroom they thought was protected, McCurdy mentioned.
Some conditions are extra nefarious. In 2025 Erin Patterson, a 51-year-old Australian girl, was sentenced to life in jail for murdering three relations and making an attempt to kill one other by deliberately feeding them a beef Wellington that included toxic fungi within the elements.
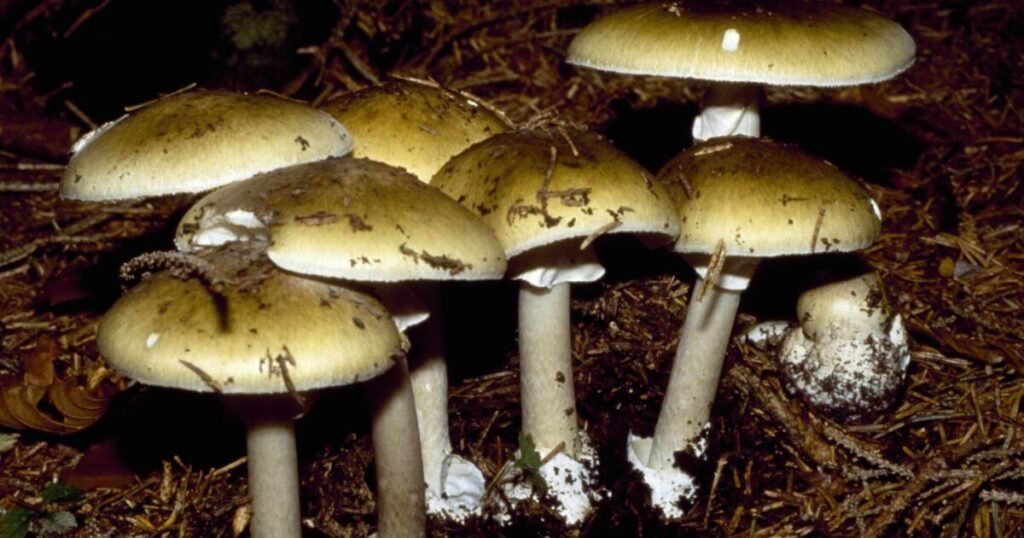
Two of essentially the most poisonous mushrooms that may be discovered within the state are the demise cap and the western destroying angel mushroom, Amanita Ocreata. Loss of life cap mushrooms have a dome-shaped cap that will have olive or yellowish tones, whereas the western destroying angel has a cream or ochre-colored cap.
Initially of Joanne Schwartz’s presentation in Newport Seaside just lately, the knowledgeable newbie mycologist acknowledged the variety of current deaths attributable to poisonous fungi.
“Guess what, these mushrooms are proper right here in Orange County,” Schwartz mentioned. “You would possibly even have one in your garden.”
She warned the roughly 20 attendees that some edible mushrooms appear to be poisonous ones, many develop aspect by aspect and if an individual collects a mushroom species in a single a part of the world, there is likely to be a lethal look-alike elsewhere.
Whereas mushroom poisonings have been concentrated additional north, phrase of the deaths and diseases has trickled right down to Southern California, sparking concern amongst those that are cautious of the spongy wonders, mentioned Rudy Diaz, president of the Los Angeles Mycological Society.
When mushroom poisonings make the headlines, individuals who aren’t part of the fungi neighborhood are likely to see those that are as being irresponsible or ruining habitats, he mentioned.
On a current hike with a good friend, Diaz mentioned he was taking a look at some mushrooms he discovered on the path and a stranger “chided me for doing one thing so dangerous.”
“For individuals who have been capable of redevelop that form of non secular reference to the land by means of their years of statement and examine, consuming issues that you simply forage is form of like an energetic communion with these environments that you simply love and also you’ve come to know,” Diaz mentioned.
However specialists, together with Diaz, say consuming mushrooms isn’t a vital a part of observing, studying and appreciating them.
For many who are properly versed in mushrooms in Southern California, there isn’t a way of alarm of attainable poisonings as a result of the poisonous mushrooms are lots much less conspicuous within the southern a part of the state.
In Northern California, demise caps are ample in native parks, “whereas right here in Southern California you need to dig by means of some oak litter earlier than you have a tendency to identify issues,” Diaz mentioned.
Nonetheless, the message from the mycology society and mycologists all through the state is one among warning: Until you’re acquainted with your native atmosphere, have an knowledgeable you possibly can seek the advice of or are a part of a mushroom or foraging membership, you shouldn’t be consuming wild mushrooms.
Mycologists use dichotomous keys to determine the species of mushroom based mostly on its bodily traits together with the cap, stem, ring and gills.
The error folks exterior the fungi neighborhood or rookies make when figuring out mushrooms is solely counting on social media, a discipline information or an app like iNaturalist, mentioned Bob Cummings, a number one mycology knowledgeable in Santa Barbara. Simply evaluating the mushroom to a photograph isn’t sufficient to make an correct species identification, he mentioned.
Schwartz inspired the general public to be energetic members in neighborhood science. Her hope, she mentioned, is that individuals get engaged with mushrooms as a result of there’s a lot to be taught in regards to the greater than 1,500 species in Orange County and over 3,000 forms of fungi within the state.
Mushrooms, poisonous or not, are OK for all to select and observe, she mentioned.
Yturralde got here away from the weekend dialogue together with his thoughts made up.
“I’m open to studying extra about mushrooms, however I’m not all for consuming something that I discover,” Yturralde mentioned. “In different phrases, I discovered that it’s finest to solely eat what’s within the [grocery store].”